Google I/O took place yesterday. The event, initially was expected to focus on Android and new software developments, but dominated by AI technologies. The company put artificial intelligence at the center of its announcements, even when introducing the new Pixel 7a, Pixel tablet, and revealing new features. However, it appears that it wasn’t enough for the tech giant. According to the latest reports, Google is making strides to integrate AI into its Chrome browser through WebGPU. Here are the details…
Google I/O Unveils AI-Ready WebGPU for Chrome Browser
Artificial intelligence technologies continue to spread and expand their use cases. However, much of the AI technology we use today runs on data centers operated by cloud computing giants like Amazon, Microsoft, and Google. This situation creates a burden on data centers and a significant expense for companies. For example, to reduce this burden, OpenAI charges users $20 per month for GPT-4 and still limits usage to 25 messages within three hours. Google plans to use the recently added WebGPU feature in Chrome to solve this problem.
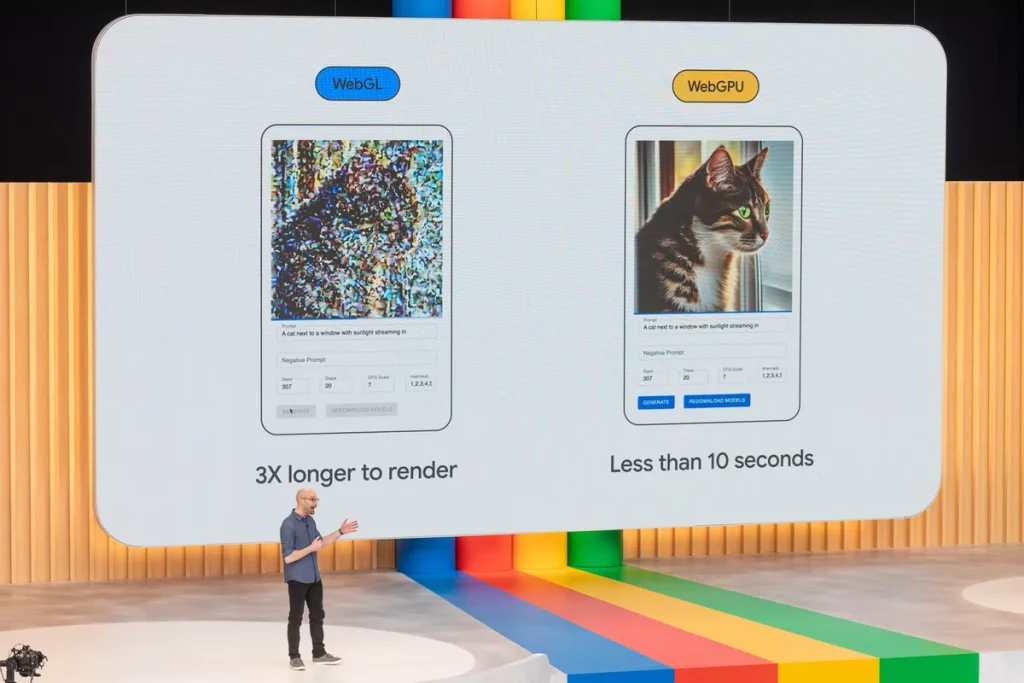
Recently released Chrome 113 comes with many innovations, including the WebGPU feature. This technology is a web standard that enhances graphics processing capabilities in web browsers. It enables more efficient execution of tasks like parallel computing, GPU acceleration, and 3D graphics, making web applications faster and more visually impressive. Another significant contribution is reducing server load by utilizing the power of your local computer.
At the Google I/O conference, it was announced that WebGPU enables web apps on phones or laptops to leverage AI software more directly. We had written the news for you yesterday when the announcement was made. This enhancement can be applied to a wide range of applications, from creative tools to health apps. “WebGPU makes the web AI-ready,” stated Matt Waddell, who leads Chrome’s developer and consumer-focused work. Running AI locally on devices like phones and laptops offers several benefits, including bypassing network issues and enabling better control over data. By doing so, Google aims to reduce the load on data centers and enhance security.
This can be particularly advantageous for businesses with sensitive data and health apps that require privacy for their users. Moreover, this is applicable for large companies as well. For instance, Samsung recently banned its employees from using AI technologies like ChatGPT due to a leak it experienced. Concerns like these could be eliminated with locally running AI tools that do not require a server. However, it remains to be seen when concerns about the increasingly widespread artificial intelligence technology will completely disappear.
RELATED:
- Best 75-inch TV in 2023 – LG, TCL, Samsung & More
- Google introduces AI tools for Play Store developers to enhance app listings
- Google Pixel Fold Debuts with a Compact Design, Tensor G2 Chip
- Google Pixel Tablet Arrives with Tensor G2 Chip, LCD display, and a Wireless dock
- Google Pixel 7a Launches with a Tensor G2 chip, Wireless charging, 64MP Camera
(via)




