It’s incredible how far smartphone technology has come in such a short time. What started as simple mobile phones designed primarily for calls has evolved into powerful mini-computers with high-resolution touchscreen displays, cameras that rival DSLRs, and features like facial recognition and intelligent assistants. Cutting-edge mobile phones from the 1990s seem downright archaic compared to what’s available today.
Given the pace of innovation, it’s fascinating to speculate what smartphones might be capable of in the future. It’s difficult to predict everything so far, but new display technology, AI integration, augmented reality, and seamless global connectivity could take these devices farther than we can currently imagine.

Holographic displays
Table of Contents
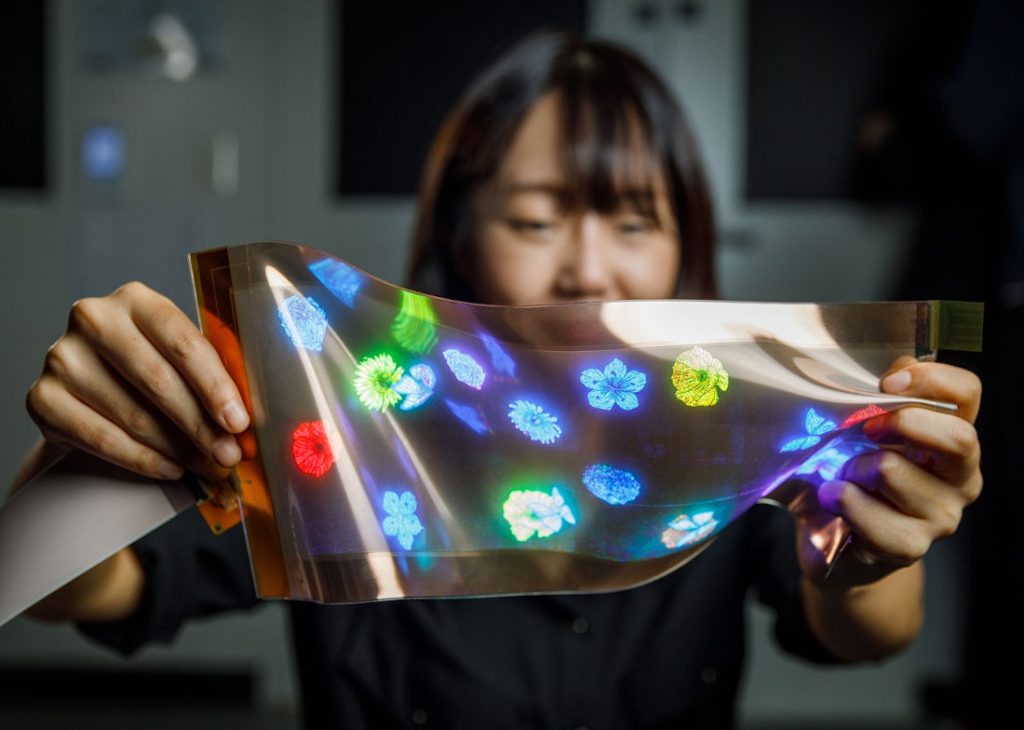
Holographic technology that projects 3D images into the air could soon make its way onto smartphones if emerging research comes to fruition. Scientists have developed light sensors that can capture and display holographic images without bulky equipment.
This breakthrough invention uses innovative photodiodes made from semiconductor materials – rhenium diselenide and tungsten diselenide. Being incorporated into a camera module, they enabled hologram capture for the first time in a compact size suitable for smartphones.
Previously, holographic cameras required large, specialized components like polarizing filters. However, by embedding the polarizing ability directly into the sensor, the need for extraneous optics is eliminated. This could allow holographic capture and display capability to be integrated into smartphones and other devices.
The applications for portable holographic tech are immense. Immersive 3D gaming, next-level augmented reality, and enhanced education features could become mainstream.
Stretchable displays
Yet another feature concerning displays. Flexible display technology has already arrived in foldable phones, but even more elastic screens could emerge in the future. Companies like LG are developing displays that can be pulled and stretched to expand screen dimensions on the fly.
Using an innovative silicon substrate and micro LEDs, these ultra-flexible prototype displays can be elongated in any direction up to 20% while maintaining full RGB color and resolution. This “rubber band-like” consistency allows the screen to comfortably stretch and snap back without damage.
For mobile devices, this could enable smartphone screens to physically expand diagonally when more viewing area is needed. A user could simply pull the corners to temporarily enlarge a 6-inch screen to 7 or 8 inches when watching videos or gaming. With flexible components, the entire phone could stretch to transform into a small tablet shape. Apps and UI elements could even adapt and rearrange themselves dynamically when stretched.
While still in their early stages, stretchable displays point to a future where screen size is no longer fixed at the time of purchase. Users could customize their portable viewing experience depending on situational needs. Though true stretchable smartphones may be years away, the technology hints at an exciting new direction for mobile innovation.

Advanced cameras
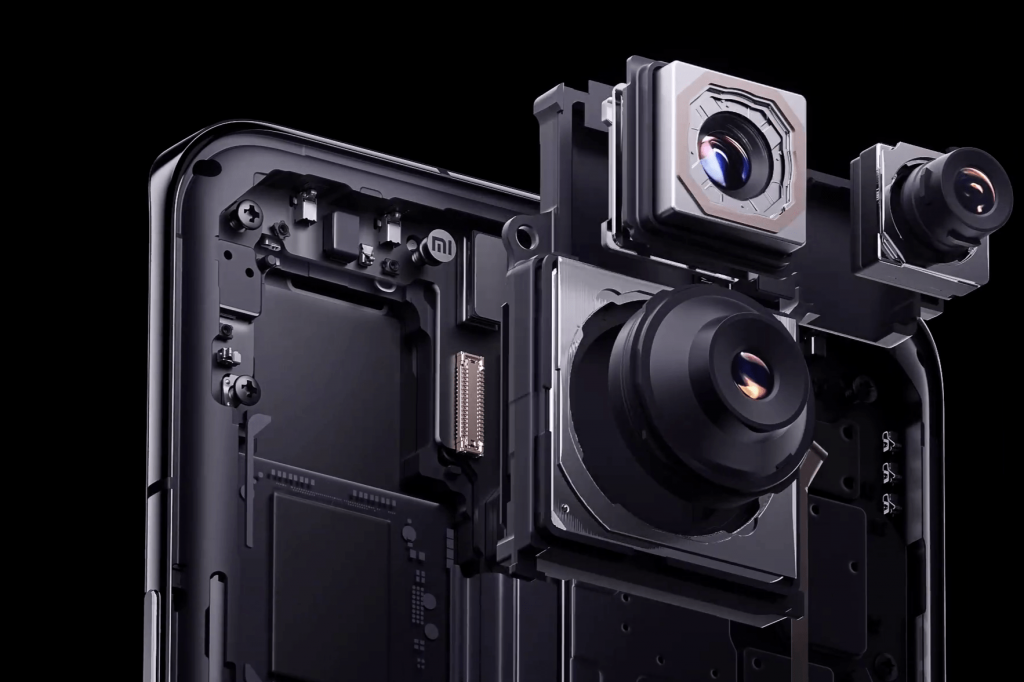
Camera hardware has progressed immensely on smartphones over the past decade. But with advancements in lens technology, sensors, AI processing, and computational photography, the camera capabilities of future phones could far surpass today’s.
Companies like Metalenz use novel nanostructures that may enable sophisticated optics in smaller modules. This could reduce the protruding camera bumps prevalent in today’s phones. Sensors will also continue to improve, with higher megapixel counts capturing more detail and low-light performance boosting image quality.
AI and dedicated imaging processors will take mobile photography to new heights. They could flawlessly stitch a multi-lens composite image or apply stunning filters indistinguishable from reality. Autofocus, HDR, portrait modes, and other automated enhancements will reach new precision with advanced machine learning.
The front-facing camera could transform with under-display solutions or unconventional form factors. For example, folding displays may allow the superior rear camera array to be used for selfies when unfolded. These capabilities could elevate selfies and video calls to mirrorless camera quality.
While standalone cameras still hold advantages, the gap between smartphones and dedicated devices will continue to narrow. One day, phones may match DSLR-level quality in a device that fits in your pocket.

eSIMs instead of SIM cards
The era of physical SIM cards may be ending as integrated eSIM technology replaces removable plastic chips. This transition, already underway at Apple and Samsung, promises more flexibility for consumers to switch networks on demand. Users could select service providers instantly based on location, deals, or needs without visiting stores for new SIM cards.
This technology also enables sleeker device designs freed from SIM trays and slots. Streamlined manufacturing without SIM components reduces costs as well.
While this technology has obstacles to overcome, the benefits of instant network switching and clutter-free designs will likely drive adoption. The familiar SIM card, a fixture of mobile life for decades, approaches its inevitable obsolescence.
Longer-lasting batteries
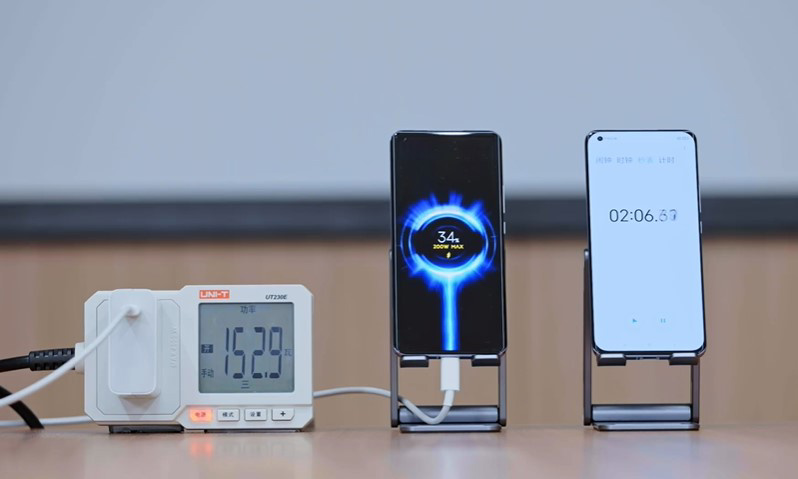
Battery limitations have long plagued smartphone users, but emerging innovations promise to finally liberate devices from daily charging. Through clever engineering and next-gen materials, future phone batteries could last days on a single charge.
Larger cell capacities will continue to drive incremental gains, but novel architectures like stacked or layered designs allow more energy storage without increasing device size. Supercapacitors offer minimal charging times measured in seconds, not hours. Their rapid charge and discharge cycles could eliminate charging anxiety.
While expectations must be tempered, continuous incremental advances along with major materials science breakthroughs could converge to finally create the long-lasting batteries smartphone users have always wanted.

Alternatives to lithium-ion batteries
And a bit more on batteries. Lithium-ion batteries have long powered our devices, but they are far from being eco-friendly. Their limitations, like short lifespans and flammability, have spurred the hunt for revolutionary replacements.
For example, advanced electrode materials like graphene can increase capacity within the same battery volume. The material’s excellent conductivity and physical features make it ideal for batteries, but exorbitant costs have restricted applications so far.
Sodium-ion batteries swap scarce lithium for abundant sodium, though slightly lower energy density results. Lithium-sulfur ones replace cobalt cathodes with sulfur, increasing capacity and lowering costs, but faster degradation remains an obstacle.
Tech leaders like Samsung develop solid-state batteries for phones. These utilize a non-flammable solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, allowing higher capacities and faster charging.

Ubiquitous wireless charging
For charging activities, batteries are just one side of the coin. There are advances in charging methods as well.
Cables for charging devices may soon become obsolete as wireless power transmission matures. Through electromagnetic field transfer, charging pads and compatible devices can wirelessly charge without contact. In the future, charging will be ubiquitous and automatic.
Inductive charging stations installed in cars, offices, restaurants, and public spaces would allow effortless topping up of phones and other electronics on the go. Resonant charging could even transmit power across entire rooms, eliminating cords altogether.
For consumers, the simplicity and convenience of omnipresent wireless technology are very important. But it has hurdles to overcome regarding energy loss over distances and safely absorbing radiation.

Improved AI and ML capabilities
Artificial intelligence and machine learning already power many convenient features in today’s smartphones, but they still have a long way to go. As algorithms become more advanced, hardware improves, and larger datasets enrich AI training, smart assistants and automation in phones could reach new heights.
Virtual assistants like Siri and Google Assistant could become nearly indistinguishable from human interactions using natural language processing. They may leverage enhanced speech recognition and synthesis for smoother conversations and understandable accents. They may also utilize context and personalization to make predictive suggestions before users even ask.
AI could manage more tasks independently, too. For example, it could automatically adjust device settings based on user habits, like dimming brightness in dark environments or enabling airplane mode in frequently visited locations. Photography will also improve through AI-enabled processing for unparalleled image and video quality.
Next-gen hardware combined with advanced algorithms will bring new real-time capabilities not possible today. Smartphones of the future could become even smarter companions that complement users’ needs and activities.
Powerful remote control capacities
Beyond just communicating and computing, future smartphones could evolve to directly interact with and control the environment around us. Advanced home automation apps would enable phones to go beyond being passive remote controls, and make them active RC devices that regulate everything from lighting to temperature.
Using integrated sensors, AI, and expanding wireless protocols like WiFi 6E and 5G, phones could monitor rooms to automatically adjust sound, lighting, climate control, security, and more to customized presets without user input. Motion sensors could activate lights and music when you enter a room, then power down when you leave.
Facial recognition via cameras could personalize environmental settings and cues to inhabitants’ preferences. Voice commands would handle intricacies hands-free. Ubiquitous wireless connectivity would enable seamless control of any networked device from your pocket.
This shift toward phones actively optimizing surrounding environments, versus just consuming content, opens new directions for convenience, accessibility, and energy efficiency.
The growth of superapps
Modern IT companies offering application development services are deepening their expertise in the field of superapps. The consolidation of services into an integrated digital product appears extremely convenient. This promises a profound transformation in how we interact with technology.
By combining an array of functions like messaging, social features, productivity, shopping, entertainment, and more into a single platform, superapps create a streamlined, one-stop experience. This convenience and simplicity appeal to consumers who are fatigued by app overload.
For businesses, these solutions present lucrative opportunities to boost revenue through diverse income streams, while also building fiercely loyal user bases. As digital ecosystems with countless touchpoints, superapps enable profound customer insights and personalized engagement.
Leading examples like WeChat dominate daily life in China, while Grab and Gojek fulfill similar roles in Southeast Asia. As the model proliferates globally, defining and refining the superapp strategy will be critical for companies seeking to capitalize on this major mobile shift.
While unlikely to completely displace specialized apps soon, this trend is gaining momentum. For both users and businesses, convergent platforms promise a more seamless, efficient, and engaging mobile experience.

6G technology
5G brought blazing-fast speeds and low latency, but 6G promises to take connectivity even further. While the 5G rollout continues globally, 6G research is already underway to outline the next major network leap.
Early 6G development indicates speeds up to 1,000 times faster than 5G, with near-zero latency enabling real-time immersive applications. Expanded bandwidth and capacity will link more devices simultaneously, from industrial IoT networks to self-driving cars.
New radio frequencies like Terahertz waves are being explored to transmit huge amounts of data faster while increasing penetration of remote areas. AI and ML will optimize 6G performance, tailoring connectivity via intelligent analysis.
Though launching commercially around 2030, 6G poses immense technical hurdles. New chipsets, antennas, infrastructure, and architectures require pioneers like Samsung, Nokia, and leading universities worldwide to lay the groundwork now.
For consumers, 6G may realize sci-fi concepts like hologram calls and digital twins. But crucially, it will also amplify 5G capabilities to empower innovative mobile experiences. While 6G’s arrival remains distant, advancing wireless generations will continue connecting smartphones and society in new ways.
Conclusion
The smartphones of today would have seemed like science fiction just a decade or two ago. Looking ahead, innovations in areas like new display forms, improved battery technology, enhanced cameras, and ubiquitous wireless charging will further enhance the capabilities of current devices. Components will become more modular and sustainable, and companion technologies like smart glasses could complement smartphones.
As engineers and researchers push the limits of what’s possible in terms of design, materials, and functionality, consumers can look forward to smartphones that integrate even more seamlessly into how we communicate, work, travel, and enjoy entertainment.




