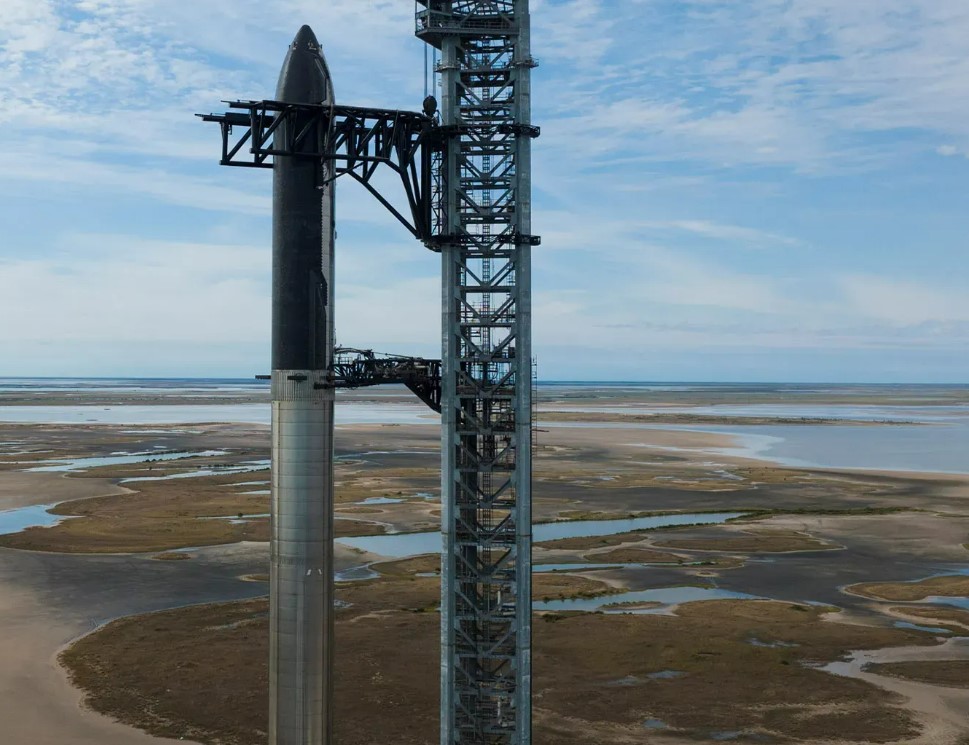
SpaceX President and COO Gwynne Shotwell, has announced that the company is all set to conduct a full static fire test on its Starship Launch Vehicle. The test will happen on 9 February and will be the first attempt at the static-fire test of all 33 engines in the Starship booster.
The Static fire test is one of the most essential parts of the final stage of technical tests conducted on the starship and is the last ground test to be conducted on the heavy-lift launch vehicle.

What is Static Fire Test?
A static fire test is a type of launch vehicle system test that helps to assess the readiness of the vehicle to reach orbit. In this test, the launch vehicle engines are filled with fuel and fired at full thrust. The vehicle is secured to the launch pad and only the engines are tested at their full capacity while the launch vehicle is clamped to the pad.
The SpaceX Starship is a launch vehicle designed to carry people and cargo to Moon, Mars, and beyond. The vehicle has a first-stage massive booster called Super Heavy and a 165-foot tall second-stage spacecraft named Starship.
The Super Heavy booster will be powered by 33 raptor engines which will be tested today at full capacity. This is a new milestone for SpaceX as it has never ignited more than 14 of its raptor engines simultaneously.
The Raptor is a group of staged combustion cycle engines, specially designed by SpaceX for Starship. The engines are fueled by cryogenic liquid methane and liquid oxygen and are more powerful than the Merlin 1D rocket engines, used in the Falcon Heavy Launch Vehicles.
Today’s static fire test is another step toward SpaceX CEO Elon Musks‘ goal of sending humans to Mars and building an interplanetary civilization. On successful completion of the static fire test, the company can get the launch license from the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration and send Starship to Orbit as early as next month.
Related:
- Elon Musk Comments on Galaxy S23 Ultra; Maybe He’s Impressed by It
- Garmin Fenix 7 Heading to Space Onboard the Polaris Dawn Space Mission
- Chinese Airspace will Soon see Flying Cars: First eVTOL Flight Permit for XPENG X2 Granted
(via)