Apple, the known smartphone maker, has bought an Edge computing based startup for a massive sum of 200 million US Dollars. A new report had surfaced after a close source to the smartphone OEM shared the information to a reporting agency called GeekWire.
Xnor.ai is an Edge computing based startup that had branched out from the nonprofit Allen Institure for AI back in 2017. Apple has confirmed the transaction of the large sum to acquire the firm. The Cupertino based giant also mentioned that it acquires smaller businesses every now and then but generally doesn’t incline in sharing the purpose or plans of the buyout.
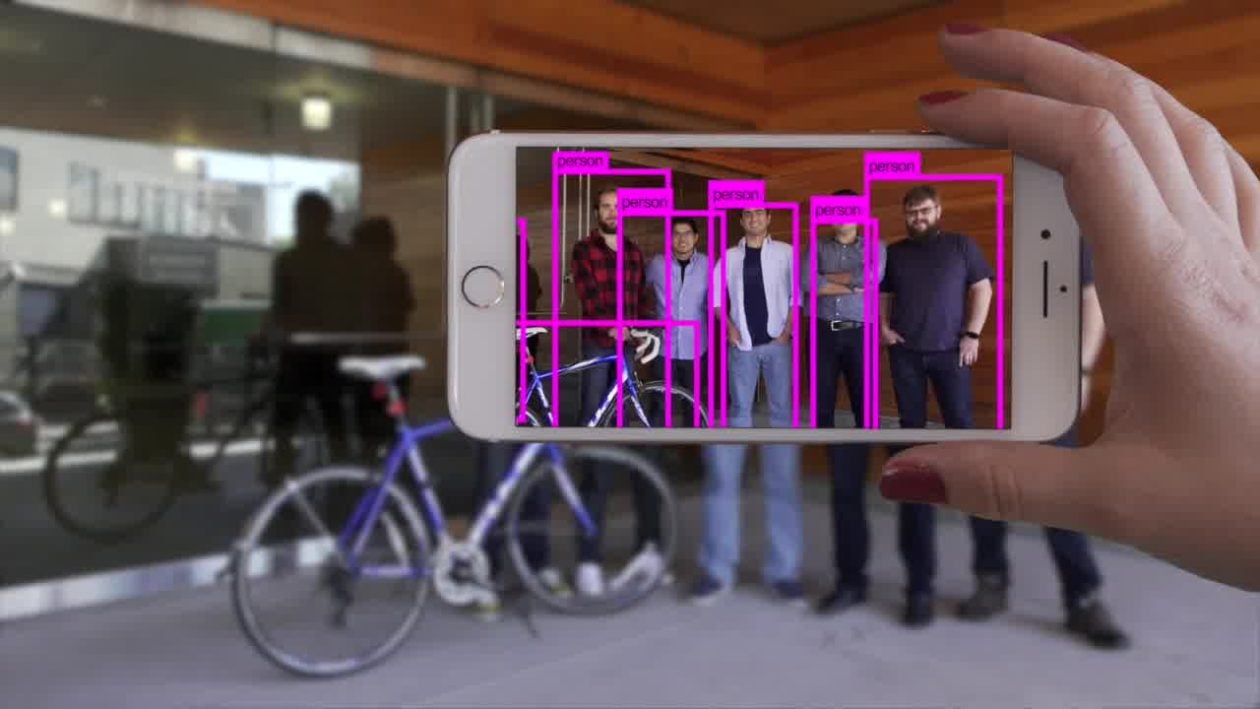
Initially, Xnor.ai focused on machine learning with efficient algorithms being developed that could run on various low tier hardware, or IoT devices (Internet of Things). This includes electronics like a security camera which consumer low amount of power to function and had a one-track streamlined function. However, with Xnor.ai’s algorithms, these gadgets could accomplish complex tasks like object recognition; which is a task that generally requires powerful processing from cloud based computer via an internet connection.
Editor’s Pick: TSMC 10nm chip shipments contributed to just 1% of wafer revenue, 7nm at 35% in Q4 2019
According to the source, the amount of 200 million US Dollars for the acquisition is just an estimate so the numbers are not concrete. Although, the numbers and investment are still ranging in tens of million which surpass any of its previous investments raised by a large margin. Xnor.ai is also expected to move to the Seattle offices of Apple which, as stated by the report.

The acquisition for an Edge computing based firm by Apple is forward thinking move from the company. Other industry giants like Google, Microsoft, and even Amazon are heavily investing in this field. With Xnor.ai, Apple plans on making its products work more independently from its cloud computing services to possibly include functions like facial recognition, natural language processing and augmented reality as well.
The implications of the field also extend towards security and privacy, since edge computing places an emphasis on local processing. Thus, Apple can make its devices more secure and even improve its imaging algorithms with machine learning. Notably, iPhones are a loose example of edge computing with local storage of biometric data (facial recognition or fingerprint scanners) and its processing.
UP NEXT: Can Redmi Note 8 survive the harsh sub-zero temperatures in Antarctica? We’ll find out soon!







