Global business solutions provider IBM has announced that it has created a 2nm chip using Gate-All-Around (GAA) nanosheet device architecture. The new transistor setup will enable IBM to fit 50 billion transistors in a tiny space the size of a fingernail. Current high-end chips like Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 888 and Apple’s A14 Bionic, use the 5nm process. However, the number of transistors that these chipsets can pack in a fingernail space does not exceed 12 billion.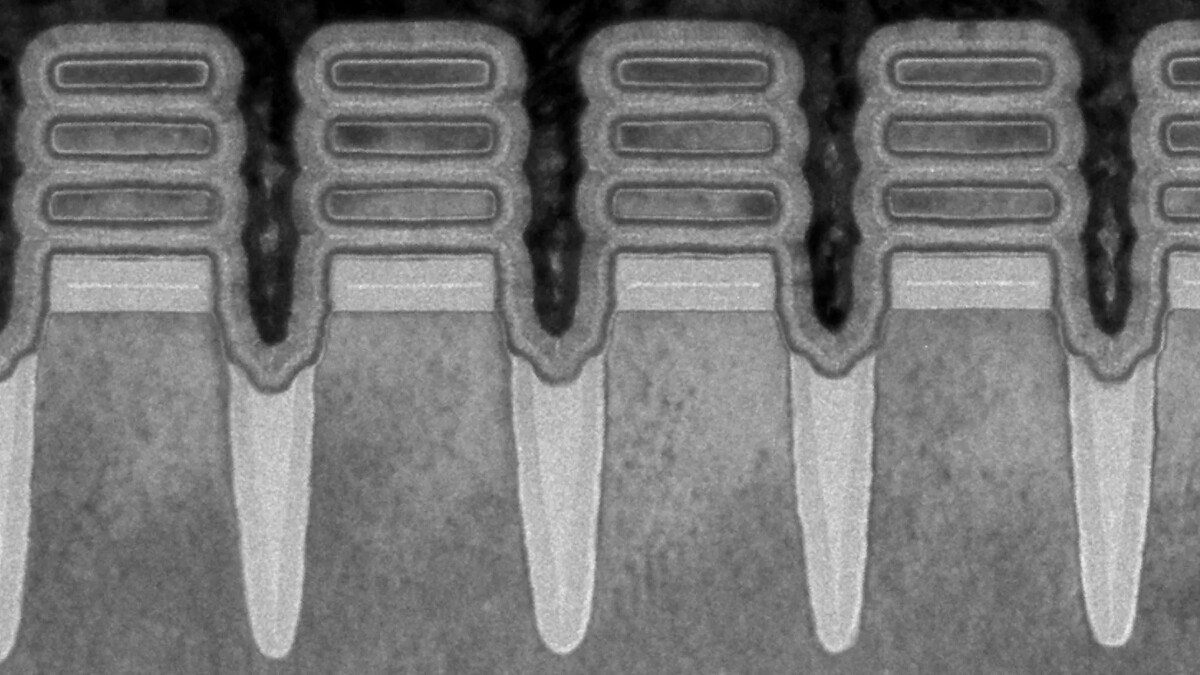
This milestone by IBM could prove to be a game-changer in the semiconductor industry. The company says battery life in smartphones deploying the 2nm technology will be greatly improved up to four times the current lifespan of batteries inside phones using the 7nm process. The implication is that, according to IBM, your smartphone will only need charging once in four days, on average.
The number of transistors that can fit in a square-mm space is an indicator of the strength and efficiency of the chip. The more powerful and energy-efficient chipset is the one that has a higher rating in this regard. There is a substantial performance increase and power savings using chips with a higher number of transistors per square mm.
The IBM concept is driven by the Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography technology. The process produces lines outside the visible light spectrum, which are used to create the patterns used to build circuits. The GAA architecture also enables superior electrical signals to pass through and between other transistors on a single chip.
IBM also says that it is actively pursuing research along the 2nm process and a rollout of the chips produced through the process is not likely in the next few years. TSMC last year revealed it is working on 2nm chips but the rollout is scheduled for 2025.
RELATED:
- Selected Lenovo laptops getting a new Alexa mode bringing Echo Show functions
- IBM patents a smartwatch that can unfold into a phone or tablet
- TSMC is working on 2nm Chips, Expected to Release by 2025






